Cylinder Engine Compression Testing for Cars Explained
Ensuring optimal performance of an automobile’s power unit is crucial for both efficiency and longevity. The evaluation of specific parameters can reveal important insights into the overall health of the engine. By examining key factors, vehicle owners and technicians can identify potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs or affect operational reliability.
Monitoring the internal condition of the engine directly impacts fuel usage, emissions, and driving experience. Engaging in systematic assessments assists in maintaining peak functionality, ultimately enhancing the lifespan of the vehicle. This proactive approach not only saves money but also guarantees safety on the road, underscoring the significance of routine evaluations.
Understanding how to carry out these evaluations effectively is essential for both professionals and enthusiasts alike. By familiarizing oneself with the techniques involved, one can ensure that the engine remains in prime condition, providing the driver with confidence and satisfaction during every journey. Knowledge in this area empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their vehicles.
The Significance of Cylinder Compression Testing
Assessing the performance and efficiency of an engine component is crucial for maintaining vehicle reliability. By examining the internal pressures, technicians can identify potential issues that may lead to reduced power output or increased fuel consumption. This evaluation serves as an essential step in ensuring optimal functionality and longevity of the engine.
Understanding the significance of this assessment includes several key aspects:
- Performance Insight: Evaluating the internal pressures provides valuable information about engine performance, helping in diagnosing problems early.
- Fuel Efficiency: By ensuring optimal function, owners can enjoy better fuel consumption, saving money in the long run.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular evaluations can help detect wear and tear, preventing more severe damage and costly repairs.
- Operational Reliability: Enhanced reliability prevents unexpected breakdowns, ensuring smoother driving experiences.
- Environmental Considerations: An efficiently functioning engine contributes to lower emissions, promoting ecological responsibility.
Overall, the analysis of internal engine pressures plays a pivotal role in vehicle maintenance strategies, leading to improved functionality and efficiency. Regular assessments are essential for all vehicle owners who prioritize performance and durability.
How Compression Affects Engine Performance
The efficient functioning of an automotive power unit relies significantly on internal pressure levels. These pressures play a crucial role in the overall performance, efficiency, and longevity of the engine. Understanding how these factors influence the operation can help maintain optimal performance and prevent potential issues.
One of the most direct impacts of this pressure is observed in the following aspects:
- Power Output: Higher internal pressures typically lead to more forceful combustion, resulting in increased power production. This enhances acceleration and overall performance.
- Fuel Efficiency: Proper pressure levels optimize fuel combustion, allowing for better fuel utilization. This leads to improved mileage and reduced emissions, making vehicles more environmentally friendly.
- Engine Longevity: Excessive or inadequate pressure can lead to premature wear and tear. Maintaining the correct levels can extend the lifespan of engine components.
Furthermore, the balance of pressures is essential for smooth operation. Variability can indicate underlying mechanical issues that, if unresolved, may lead to severe damage.
- Monitor the levels regularly.
- Address any discrepancies promptly.
- Utilize quality fuels and maintenance practices.
In conclusion, maintaining optimal internal pressures is vital for enhancing power, efficiency, and durability. Understanding these relationships equips vehicle owners with the knowledge necessary to keep their engines running smoothly.
Benefits of Regular Compression Checks
Conducting routine evaluations of the internal pressure within an engine can greatly enhance vehicle performance and longevity. These assessments provide valuable insights into the engine’s condition, allowing for timely maintenance and repairs. By identifying potential issues early on, drivers can avoid more significant problems that may arise from neglect.
Enhanced Engine Performance: Regular assessments support optimal engine functionality, ensuring that power delivery is smooth and efficient. This leads to improved acceleration and overall driving experience.
Fuel Efficiency: Monitoring pressure levels can help in recalibrating engine components, which can result in better fuel consumption. A well-maintained engine uses fuel more efficiently, saving money at the pump.
Longevity of Engine Components: Regular scrutiny can spot wear and tear early, allowing for proactive repairs. This not only extends the life of the engine but also reduces the frequency of major overhauls.
Cost Savings: By addressing minor issues before they escalate, drivers can save significantly on repair costs. Preventive measures often come at a fraction of the expense compared to major repairs due to neglect.
Emissions Control: Keeping the engine in prime condition helps in reducing harmful emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment. Regular evaluations ensure that the vehicle complies with environmental regulations.
In conclusion, consistent monitoring of engine pressure offers multiple advantages, from improved efficiency to cost savings. These checks are a vital part of responsible vehicle maintenance.
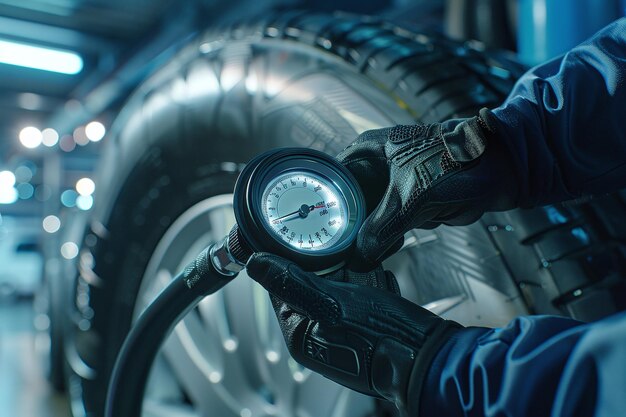
Essential Tools for Compression Testing
A successful evaluation of an engine’s performance relies heavily on the appropriate instruments and equipment. The selection of the right tools is vital for accurately assessing the condition of internal mechanisms and ensuring reliable results. Without the necessary resources, it becomes challenging to draw meaningful conclusions regarding engine health.
Key Instruments Needed
To begin with, a quality gauge should be at the top of the list. This instrument measures pressure levels and provides critical data about engine efficiency. Additionally, a portable air source is essential to ensure consistent readings and avoid external influences that might skew results. Tools for sealing off the various openings in the engine are also crucial, as they help contain necessary pressures during evaluation.
Supporting Equipment
Furthermore, having a reliable set of hand tools, such as wrenches and sockets, allows for proper installation and removal of components in a hassle-free manner. A high-precision torque wrench is also beneficial to maintain adequate specifications while assembling parts. Lastly, a comprehensive service manual specific to the vehicle in question can offer invaluable guidance throughout the entire evaluation process.
Step-by-Step Compression Testing Procedure
This section outlines a systematic approach designed to evaluate engine efficiency through a series of precise actions. Each stage is crucial for obtaining accurate measurements and ensuring that the power unit operates optimally.
Preparation
- Gather necessary tools and equipment, including a pressure gauge and spark plug socket.
- Ensure the engine is cool and parked on a level surface.
- Disconnect the battery to prevent accidental starts.
Execution
- Remove the spark plugs from the engine’s head.
- Insert the pressure gauge into the spark plug hole for the first chamber.
- Activate the starter motor for a few seconds to allow the gauge to record the value.
- Note the reading and then disconnect the gauge.
- Repeat the process for each chamber in the engine.
- Compare the obtained results to the manufacturer’s specifications to assess wear and sealing integrity.
Interpreting Compression Test Results
Understanding the results from a pressure evaluation is crucial for diagnosing engine health. These measurements provide insight into the functioning of the engine’s internal components, helping mechanics and car owners alike identify potential issues before they escalate. A thorough interpretation of these results reveals the overall performance and efficiency of the engine, guiding necessary maintenance decisions.
Analyzing the Values
When assessing the gathered values, it is essential to compare them to the manufacturer’s specifications. Typically, a healthy engine will show uniform pressure levels across all measured units. A significant disparity may indicate mechanical wear, improper sealing, or even some form of damage. If the values are below the expected range, it could signify problems like worn piston rings, valve leakage, or gasket failures. Conversely, exceptionally high levels may point to underlying issues such as carbon buildup or improper assembly.
Understanding Imbalances
It is important to consider the relationship between each unit’s values. An engine exhibiting uneven readings across its components may suggest specific localized problems, such as a malfunctioning valve or a damaged cylinder head. Noting which units share similar readings can also help pinpoint areas of concern. Taking additional measurements, including a leak-down assessment, can provide further clarity and confirm initial findings.
In conclusion, a meticulous examination of evaluation outcomes empowers vehicle owners to make informed decisions regarding their engine’s maintenance. Recognizing patterns in the values, as well as understanding individual readings, leads to proactive care and ultimately extends the lifespan of the engine.
Common Issues Revealed by Testing
Evaluating engine performance using standardized checks can uncover various underlying problems that may not be immediately visible. These assessments can reveal significant discrepancies in engine health, contributing to improved efficiency and longevity when addressed promptly. Understanding these potential complications is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle function.
Key Problems Identified
The following table outlines frequent issues discovered during evaluations, along with brief explanations:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Worn Rings | Indicates loss of seal, leading to pressure loss and reduced power output. |
| Piston Damage | Can result from overheating or inadequate lubrication, often linked to excessive wear. |
| Valve Failures | Leaks can occur if valves do not close properly, affecting overall engine performance. |
| Head Gasket Issues | Can cause coolant and oil mixing, leading to potential engine overheating and failure. |
| Poor Sealing | May stem from aging components, contributing to overall inefficiency and performance loss. |
Importance of Regular Evaluations
Regular assessments are essential in identifying these issues early, ensuring timely repairs and maintenance. Proactively managing engine condition contributes to better fuel efficiency, enhanced power delivery, and prolonged vehicle lifespan, ultimately providing a more reliable driving experience.
Q&A: Cylinder compression test for cars
What does it mean to “crank the engine” when checking compression?
When you “crank the engine,” you are turning the engine over using the starter motor to build pressure in the cylinders for a compression reading.
How can you determine if an engine has “low compression”?
To determine if an engine has “low compression,” you can use a compression gauge to measure the psi in each cylinder. A reading significantly below the manufacturer’s specifications indicates low compression.
What is the purpose of a “compression tester”?
A compression tester is used to measure the psi in each cylinder of an engine, helping diagnose issues related to low compression, such as worn piston rings or valve seat problems.
Why is it important to “disable the ignition” before testing compression?
Disabling the ignition prevents the engine from starting while you crank it, ensuring safety and accurate compression readings without interference from the ignition system.
What should you expect if you get a “compression reading” of 100 psi?
A compression reading of 100 psi may indicate that there are issues with one cylinder, suggesting potential problems with the piston rings, valves, or head gasket.
How do you use a “compression gauge” correctly?
To use a compression gauge, remove the spark plug from one cylinder, screw in the gauge, and then crank the engine to obtain the psi reading for that cylinder.
What role does the “fuel pump” play when testing engine compression?
The fuel pump should be disabled during a compression test to prevent fuel from entering the cylinders, which could affect the accuracy of the compression readings.
What is a common symptom of “low compression” in an engine?
Common symptoms of low compression include rough idling, difficulty starting, loss of power, and increased exhaust smoke, indicating potential issues with one cylinder.
How does a faulty “coil” affect engine performance related to ignition?
A faulty coil can lead to weak or inconsistent spark delivery to the spark plugs, affecting ignition and potentially causing low compression issues due to incomplete combustion.
What is the significance of checking “engine oil” levels before performing a compression test?
Checking engine oil levels is important because low oil can indicate underlying issues that might contribute to low compression, such as excessive wear or oil leaks affecting one cylinder.
To perform a compression test, what are the initial steps needed to prepare the vehicle’s engine?
First, ensure the engine is warm for accurate readings. Then, disable the ignition system and remove the fuel pump fuse to prevent fuel from entering the combustion chamber during the test.
How do you use a compression gauge to get a compression reading from a single cylinder?
You need to thread the compression gauge into the spark plug hole of the cylinder of the engine you are testing. Then, turn the engine over to perform the test and record the psi or higher reading.
What does it mean if one cylinder has low compression compared to others?
If one cylinder has low compression, it may indicate issues such as a blown head gasket, worn piston rings, or an exhaust valve problem, leading to compression loss in that specific cylinder.
What is the significance of performing a leak down test after finding low compression in a diesel engine?
A leak down test measures how well air is retained in the cylinder during the compression stroke, helping identify where the compression loss is occurring inside the engine, such as through valves or cylinder walls.
How does the compression ratio affect engine performance, especially in diesel engines?
The compression ratio determines how much air is compressed before fuel injection, affecting power output and efficiency. A higher compression ratio typically leads to better performance but may also increase the risk of knocking.
What should you check if the check engine light comes on after performing a compression test?
If the check engine light activates, it could indicate underlying engine issues related to low compression in one or more cylinders. A diagnostic scan can help pinpoint specific trouble codes linked to the problem.
Why is it important to disable the fuel pump before testing compression?
Disabling the fuel pump prevents fuel from entering the combustion chamber, ensuring that only air is compressed during the test, which provides an accurate measure of the engine’s compression.
What role does the timing belt play when performing a compression test?
The timing belt ensures that the engine’s valves open and close at the correct times. If it’s damaged or misaligned, it can lead to improper valve operation and affect compression readings during the test.
How can you determine if there is an issue with the intake and exhaust valves when testing compression?
If testing shows low compression in a cylinder, you can perform a leak down test to see if air escapes through the intake or exhaust valves, indicating potential issues with those engine parts.
What are typical psi readings expected for proper compression in a diesel engine?
For a diesel engine, proper compression is generally expected to be 300 psi or higher per cylinder. Readings below this may indicate issues requiring further investigation.